Oral Cavity Cancer, Lip and Oropharyngeal Cancer
Introduction
Malignancies of the tongue represent one of the greatest management challenges for the head and neck oncologist because of the adverse effects of treatment on oral and pharyngeal function, the eventual quality of life, and the poor prognosis of advanced disease. The unique behavior of these tumors also requires aggressive management to minimize the risk of locoregional spread.
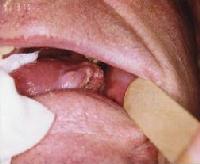
Clinical appearance of a lateral tongue squamous cell carcinoma in an 80-year-old man with a previous history of smoking and regular alcoholic beverage consumption.
Frequency
The tongue is the most common intraoral site of cancer in most countries. The worldwide incidence of oral cancer varies widely. Because of this variability, cancer of the tongue is a serious public health problem with significant mortality and morbidity.
Cancers of the oral cavity represent 2% of all cancers diagnosed annually in the United States. The disease affects males more frequently than females, with a male-to-female ratio of 2:1.
In Europe and Australia, the incidence of oral cavity cancer is very low, accounting for less than 5% of all cancers. In France (male incidence rates up to 8 per 100,000 per annum), it is the third most common cancer in males and the second most common cause of death from cancer. In India, the incidence rate approaches 50% (male incidence rates up to 6.5 per 100,000 per annum).
This incidence variability may relate to different societal habits, such as chewing betel nuts and habitual reverse smoking observed in Asia and the higher incidence of smoking and alcohol intake in certain European countries.
EtiologyTobacco
Of all potential etiologic factors, cancer of the tongue is correlated the closest with the use of tobacco products. Numerous studies have shown that up to 90% of patients with oral cavity cancers use tobacco products and that the relative risk of such cancers increases with the amount smoked and the duration of the habit. The incidence of oral cavity cancers in persons who smoke is approximately 6 times that of those who do not smoke. Exposure to tobacco causes progressive sequential histological changes to the oral mucosa. Over a prolonged period of exposure, these changes eventually lead to neoplastic transformation. These changes may be reversible if tobacco exposure is discontinued.
The recent increase in the incidence of oral cavity cancer in young adults is significant. The explosive use of snuff, or smokeless tobacco, in certain regions of the United States has lead to increased numbers of buccal mucosa, mandibular alveolus, and tongue cancers.
Alcohol
The correlation between alcohol consumption, particularly hard liquor, and oral cavity cancer is also significant, especially in patients taking more than 4 consumptions per day. Approximately 75% of patients who develop oral cavity cancers consume alcohol, and the disease occurs 6 times more often in persons who drink than in those who do not drink. The role of alcohol consumption in the development of tongue cancer appears to be independent of cigarette smoking. The use of alcohol has a synergistic rather than cumulative effect on the risk of carcinogenesis. The risk for a person who smokes tobacco and drinks alcohol is 15 times that of an individual with neither habit.
Other factors
A number of other factors have been associated with an increased incidence of tongue cancer. The use of betel nuts or quid and slaked lime is a habit practiced by as many as 220 million people in India and the continent of Asia. This mixture is highly irritating to the oral mucosa.
Plummer-Vinson syndrome, which includes iron deficiency, has been associated with an increased risk of cancer of the oral cavity. Increasing amounts of data suggest that vitamins A and C, along with the carotenoids, may be protective against epithelial cancers.
The detection of mutations in tumor suppressor genes has been reported in patients with cancers of the oral cavity. Nitrosamines constitute the most abundant carcinogens present in tobacco. These agents can damage DNA, leading to point mutations. These point mutations lead to deregulation of tumor suppressor genes, the best characterized being TP53, which is located on chromosome 17. Other oncogenes associated with oral squamous cell cancers include c-myc and erb -b1.
The human papillomavirus, an epitheliotropic DNA virus, is another possible etiologic agent for carcinogenesis, transforming cells to a malignant phenotype. Human papillomavirus has been detected in various amounts in persons with oral dysplasia, leukoplakia, and malignancy. See also Human Papillomavirus. Riboflavin and iron deficiencies are known to produce dysplastic changes to the oral mucosa. This may partly explain its relationship to alcoholism, which may result in riboflavin deficiency and oral cancer.
The role of occupational and environmental exposures in the development of cancer is an expanding field of study and may eventually be more important once the underlying molecular biology of cancer is better understood.
Pathophysiology
As with other areas of the upper aerodigestive tract, more than 90% of oral cavity cancers are squamous cell carcinomas. Most of the other lesions are of minor salivary gland origin. Lymphomas, melanomas, and sarcomas rarely occur in the tongue. The following information, unless otherwise stated, is related to squamous cell carcinomas.
Premalignant lesions
Leukoplakia and erythroplakia are the lesions with the greatest potential for malignant transformation. The term leukoplakia is defined as a clinical white patch of the mucosa that cannot be characterized clinically or pathologically as any other disease. Leukoplakia is considered a premalignant condition from the chronic irritation of the mucous membranes, resulting in increased rates of epithelial and connective tissue proliferation. Onset of leukoplakia generally occurs after age 40 years, with the incidence peaking before age 50 years. It is 2-3 times more common in men than in women.
The fate of leukoplakic lesions has been the subject of much controversy. The rates of malignant transformation range from less than 1% to as high as 17.5%, averaging 4.5-6%. In one of Banoczy's studies, a cohort of 670 patients was monitored for 3 years; of the patients, 7.5% had spread of leukoplakia in the oral cavity and 6% of the lesions became malignant.1 Leukoplakia erosiva (erythroleukoplakia) and nodular leukoplakia exhibited the highest rate of malignant transformation.
Erythroplakia is defined as a red, velvety plaque that is found on the oral mucosa and cannot be ascribed to any other predetermined condition. No sex predilection is recognized, and it is rarely found on the tongue compared with other sites in the oral cavity. Mashberg has considered erythroplakia the earliest sign of asymptomatic cancer
.Squamous cell carcinoma
Squamous cell carcinoma is by far the most common malignancy of the tongue, typically having 3 gross morphologic growth patterns: exophytic, ulcerative, and infiltrative. The infiltrative and ulcerative types are observed most commonly on the tongue. Early carcinomas smaller than 1 cm may be detected only during a routine clinical examination. In the case of symptomatic tumors, the most common finding is an indurated, ulcerated area of the tongue. The induration may extend deep into the tongue musculature and root of the tongue. In many cases, regional lymphadenopathy may be present. Generally, a correlation is recognized between tumor size, nodal presence, metastasis, and eventual prognosis. The relationship between histological differentiation and clinical stage of the illness has been the subject of debate. Currently, the site and size of the primary tumor are well recognized as factors that are more important.
PresentationMalignancies of the tongue may grow to significant size before they cause symptoms. Approximately three fourths of the cancer occurs in the mobile tongue and is most often well differentiated. Because of the relative laxity of the tissue planes separating the intrinsic tongue musculature, the cancer may spread easily and become symptomatic only when its size interferes with movement. Squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue may arise in apparently normal epithelium, in areas of leukoplakia, or in an area of chronic glossitis. These lesions are usually larger than 2 cm at presentation, with the lateral border being the most common subsite of origin. At this point, the patient may develop speech and swallowing dysfunction. Pain occurs when the tumor involves the lingual nerve, and this pain may also be referred to the ear.
Carcinomas of the tongue base are clinically silent until they deeply infiltrate the tongue musculature. They are usually less differentiated. Because of the difficulties with direct visualization, they may extend into the oral tongue or have clinical lymph metastases before the diagnosis is established.
The evaluation of a patient with tongue cancer begins with a detailed history, specifically inquiring about tobacco and alcohol use, pain, weight loss, dysphagia and odynophagia, referred otalgia, hemoptysis, hoarseness, and articulation difficulties. During a complete head and neck examination, specific attention is directed at the site and size of the lesion and infiltrating characteristics; furthermore, the physician should perform a thorough bimanual examination of the tumor, the surrounding floor of mouth, and the submandibular triangles. Nodal adenopathy is carefully noted with the manual examination of the neck and is compared to imaging studies obtained as part of the evaluation.
A dental evaluation is also performed, with attention to dental hygiene, dentition status, and integrity of the mandible. Patients with additional medical problems or those who will likely have complications should be referred for evaluation by an internist or an appropriate subspecialist. Because surgery is often part of the therapy of these lesions, an opinion from a medical internist may be obtained to aid in the perioperative treatment of the patient.
Relevant Anatomy
The oral tongue is the freely mobile portion of the tongue. It is bordered anteriorly by the lingual frenulum and posteriorly by the circumvallate papillae. The root is the undersurface of the tongue at its junction with the floor of the mouth. The junction of the tongue with the floor of the mouth forms a gutter, the gingivolingual sulcus, where food and liquids flow to the oropharynx. The oral tongue consists of 4 anatomic regions: the tip, the lateral borders, the dorsum, and the undersurface. Posterior to the circumvallate papillae, the base of the tongue is anatomically part of the oropharynx. It is covered by squamous epithelium composed of circumvallate, filiform, and fungiform papillae.
The muscular portion of the tongue is composed of 3 paired intrinsic and 3 paired extrinsic muscle groups. The extrinsic muscles, made up of the genioglossus, hyoglossus, and styloglossus, alter the shape and position of the tongue. The trilaminar group of intrinsic muscles, which is composed of the inferior lingual, vertical, and transverse muscles, originates and inserts within the tongue substance. They are responsible for the changes in the shape of the tongue during speech, mastication, and swallowing.
The lingual artery provides blood supply to the tongue. A branch of the external carotid artery, it arises at the level of the hyoid, where it travels forward to lie deep to the hyoglossus muscle. At this point, it divides into various branches to supply the ipsilateral tongue. Its only anastomosis is with its contralateral artery at the tongue tip. A plexus of veins follows the artery, and the main lingual vein drains into the internal jugular vein.
The hypoglossal (cranial nerve XII) nerve runs anteriorly between the submandibular gland and the hyoglossus muscle. Nerve fibers are sent to the extrinsic muscles; then, the terminal branches plunge into the tongue substance to supply the intrinsic muscles. The lingual branch of the mandibular nerve (cranial nerve V3) provides the sensory nerve supply. Taste is provided by the chorda tympani, a branch of the facial nerve, traveling with the lingual nerve.
Because of its different embryological origin, the glossopharyngeal (cranial nerve IX) nerve and the superior laryngeal nerve, which provide sensation, motor supply, and taste, supply the base of the tongue.
An extensive submucosal lymphatic plexus provides lymphatic drainage to the tongue. All vessels ultimately drain into the deep jugular lymph nodes, between the levels of the digastric and omohyoid muscles. Various lymphatic collection channels originate near the tongue tip, pierce the mylohyoid, and drain into first echelon submental and submandibular lymph nodes. Lymph node channels from the tongue base pass through the pharyngeal wall laterally below the tonsil to reach the jugulodigastric nodes. Because the lymphatic plexus freely communicates across the midline, cancer of the tongue frequently metastasizes bilaterally.
Contraindications
Contraindications to surgery for tumors of the mobile tongue include patients who are unable to tolerate anesthesia for such a procedure because of medical illness. In certain cases, patients may not be suitable for surgery if the tumor is deemed unresectable on the basis of its extent. Surgery would also be contraindicated in a patient refusing a surgical procedure.
Because of the difficulty in tolerating anesthesia, these patients would also not be suitable candidates for brachytherapy. In these cases, such patients should be considered for external beam radiation therapy.